免职声明:本网站为公益性网站,部分信息来自网络,如果涉及贵网站的知识产权,请及时反馈,我们承诺第一时间删除!
This website is a public welfare website, part of the information from the Internet, if it involves the intellectual property rights of your website, please timely feedback, we promise to delete the first time.
电话Tel: 19550540085: QQ号: 929496072 or 邮箱Email: Lng@vip.qq.com
摘要:目前,在页岩油气水平井钻井中,油基钻井液以优异的井壁稳定性和润滑性仍占据主导地位,但是环保和成本方面的压力也越来越大。国内外开展了大量高性能水基钻井液创新研究,部分体系已收到较好应用效果。国外MI-SWACO、哈里伯顿、贝克休斯等公司开发了一系列强抑制强..
|
目前,在页岩油气水平井钻井中,油基钻井液以优异的井壁稳定性和润滑性仍占据主导地位,但是环保和成本方面的压力也越来越大。国内外开展了大量高性能水基钻井液创新研究,部分体系已收到较好应用效果。国外MI-SWACO、哈里伯顿、贝克休斯等公司开发了一系列强抑制强封堵页岩水基钻井液体系,不同区域应用占比为15%~40%。
页岩水基钻井液在井壁稳定、润滑性等方面取得一定的应用效果,但仍面临三大挑战。一是页岩储层裂隙发育、井壁极易失稳,现有体系的封堵能力还不能完全满足需要;二是针对页岩油气储层黏土含量高,现有体系抑制黏土水化膨胀或分散能力有待进一步加强,有害固相去除困难,钻井液清洁程度不高;三是页岩油储层钻进中常遇原油污染,钻井液黏切剧增,缺乏有效处理措施,油侵严重时只能置换钻井液。 At present, in the drilling of shale oil and gas horizontal Wells, oil-based drilling fluids still play a dominant role with excellent wall stability and lubricity, but the pressure of environmental protection and cost is also increasing. A lot of innovative research on high-performance water-based drilling fluid has been carried out at home and abroad, and some systems have received good application results. Foreign companies such as MI-SWACO, Halliburton and Baker Hughes have developed a series of strong inhibition and strong sealing shale water-based drilling fluid systems, which account for 15% to 40% of applications in different regions. In recent years, domestic major oil companies have carried out targeted research from shale formation wellbore instability mechanism, water-based drilling fluid system construction, field application and other aspects, and developed different characteristics of shale water-based drilling fluid systems. Chuanqing Drilling Company developed CQH-M1, CQH-M2 high-performance water-based drilling fluids, and applied more than 50 Wells in Changning, Weiyuan and other blocks. The organic salt-water based drilling fluid system developed by Zhejiang Oilfield has been successfully applied in Dazhai shale gas field, Luzhou, Sichuan. Zhongyuan Petroleum Engineering developed ZY-APD shale water-based drilling fluid and NAPG (alkyl glycosides) oil-based drilling fluid, and applied 3 Wells in Jinjinba block in southern Sichuan. Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Engineering Technology developed two sets of high-performance shale water-based drilling fluid systems, among which SM-ShaleMud-1 carried out pilot tests on six Wells of Weiye 23 platform. The drilling fluid density reached 2.15 g/cm ³ and the bottom hole temperature reached 140 degrees Celsius. Set a number of records such as the length of the open hole section, 2115 meters, and the penetration of the horizontal section, 1500 meters. SM-ShaleMud-II has been applied in 8 Wells such as Shuaiye 3-7HF and Qinjye 2HF in northern Jiangsu shale oil field. Shale water-based drilling fluid has achieved certain application results in wellbore stability and lubricity, but it still faces three major challenges. Firstly, the fracture development of shale reservoir and the wellbore instability are easy, and the plugging capacity of the existing system can not fully meet the needs. Second, due to the high clay content in shale oil and gas reservoirs, the existing system's ability to inhibit the hydration expansion or dispersion of clay needs to be further strengthened, the removal of harmful solid phase is difficult, and the cleaning degree of drilling fluid is not high. Third, oil pollution often occurs in shale oil reservoir drilling, resulting in sharp increase in drilling fluid viscosity, lack of effective treatment measures, and can only replace drilling fluid when oil invasion is serious. |
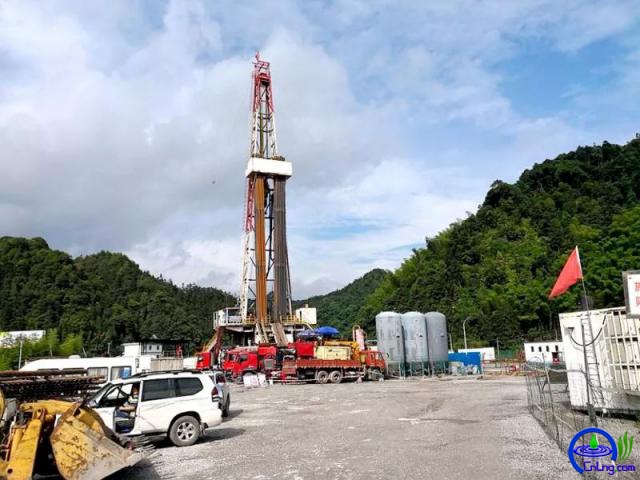


 近年来,国内各大石油公司从页岩地层井壁失稳机理、水基钻井液体系构建、现场应用等方面开展了针对性研究,开发了各具特色的页岩水基钻井液体系。川庆钻探公司研发出CQH-M1、CQH-M2高性能水基钻井液,在长宁、威远等区块规模化应用50余口井;浙江油田研制的有机盐水基钻井液体系在四川泸州大寨页岩气田应用成功;中原石油工程研制了ZY-APD页岩水基钻井液和NAPG(烷基糖苷)类油基钻井液,在川南地区黄金坝区块应用3口井。中国石化石油工程技术研究院研制了两套高性能页岩水基钻井液体系,其中SM-ShaleMud-1在威页23平台的6口井开展先导试验,钻井液密度达到2.15克/立方厘米,井底温度高达140摄氏度,创造裸眼段长2115米、水平段进尺1500米等多项纪录;SM-ShaleMud-II在苏北页岩油帅页3-7HF、溱页2HF等8口井进行了规模化应用。
近年来,国内各大石油公司从页岩地层井壁失稳机理、水基钻井液体系构建、现场应用等方面开展了针对性研究,开发了各具特色的页岩水基钻井液体系。川庆钻探公司研发出CQH-M1、CQH-M2高性能水基钻井液,在长宁、威远等区块规模化应用50余口井;浙江油田研制的有机盐水基钻井液体系在四川泸州大寨页岩气田应用成功;中原石油工程研制了ZY-APD页岩水基钻井液和NAPG(烷基糖苷)类油基钻井液,在川南地区黄金坝区块应用3口井。中国石化石油工程技术研究院研制了两套高性能页岩水基钻井液体系,其中SM-ShaleMud-1在威页23平台的6口井开展先导试验,钻井液密度达到2.15克/立方厘米,井底温度高达140摄氏度,创造裸眼段长2115米、水平段进尺1500米等多项纪录;SM-ShaleMud-II在苏北页岩油帅页3-7HF、溱页2HF等8口井进行了规模化应用。







