免职声明:本网站为公益性网站,部分信息来自网络,如果涉及贵网站的知识产权,请及时反馈,我们承诺第一时间删除!
This website is a public welfare website, part of the information from the Internet, if it involves the intellectual property rights of your website, please timely feedback, we promise to delete the first time.
电话Tel: 19550540085: QQ号: 929496072 or 邮箱Email: Lng@vip.qq.com
摘要:Abstract Swelling and shrinkage (volumetric change) of coal during adsorption and desorption of gas is a well-known phenomenon. For coalbed methane recovery and carbon sequestration in deep, unminable coal beds, adsorption-induced coal volumetric ..
|
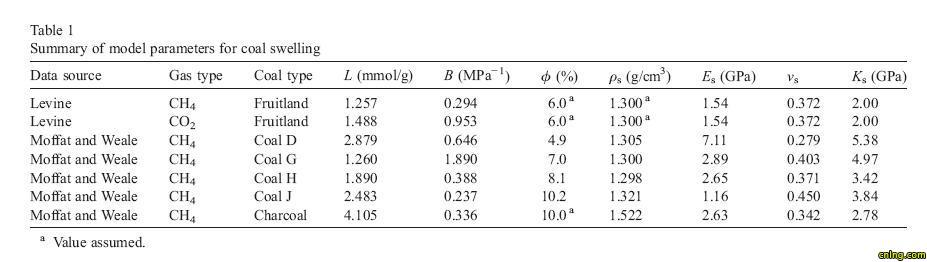
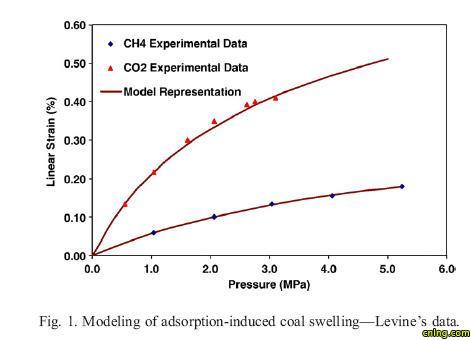
Abstract Swelling and shrinkage (volumetric change) of coal during adsorption and desorption of gas is a well-known phenomenon. For coalbed methane recovery and carbon sequestration in deep, unminable coal beds, adsorption-induced coal volumetric change may cause significant reservoir permeability change. In this work, a theoretical model is derived to describe adsorption-induced coal swelling at adsorption and strain equilibrium. This model applies an energy balance approach, which assumes that the surface energy change caused by adsorption is equal to the elastic energy change of the coal solid. The elastic modulus of the coal, gas adsorption isotherm, and other measurable parameters, including coal density and porosity, are required in this model. Results from the model agree well with experimental observations of swelling. It is shown that the model is able to describe the differences in swelling behaviour with respect to gas species and at very high gas pressures, where the coal swelling ratio reaches a maximum then decreases. Furthermore, this model can be used to describe mixed-gas adsorption induced-coal swelling, and can thus be applied to CO2-enhanced coalbed methane recovery.
|