免职声明:本网站为公益性网站,部分信息来自网络,如果涉及贵网站的知识产权,请及时反馈,我们承诺第一时间删除!
This website is a public welfare website, part of the information from the Internet, if it involves the intellectual property rights of your website, please timely feedback, we promise to delete the first time.
电话Tel: 19550540085: QQ号: 929496072 or 邮箱Email: Lng@vip.qq.com
摘要:A. During the filling process, a LNG nozzle is hooked up to a receptacle on the vehicle. Once the connection is made and the dispenser button is pushed, the liquefied natural gas starts to flow through the nozzle and the check valve and into the s..
|
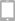
A. During the filling process, a LNG nozzle is hooked up to a receptacle on the vehicle. Once the connection is made and the dispenser button is pushed, the liquefied natural gas starts to flow through the nozzle and the check valve and into the spray header.
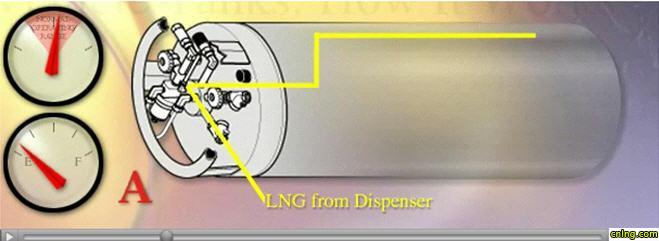
B. As the liquefied natural gas is spraying out of the header, the very cold mist starts to condense the slightly warmer vapor in the tank. As the vapor condenses it also contracts in volume, lowering the head pressure within the tank. This process is referred to as “collapsing head pressure.”
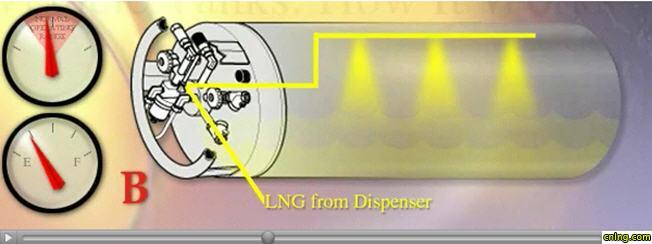
C. As the collapsing of the head pressure occurs, the fuel liquid level continues to rise until it reaches the spray header. As the liquid level approaches the spray header, the misting has less and less effect on the vapor portion of the fuel since the amount of vapor volume is decreasing and the mist does not have as much contact area before coming into contact with the liquid.
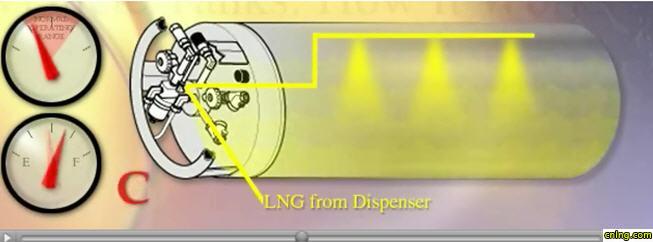
D. Once the liquid level has reached the spray header, the head pressure quickly rises. The fueling station senses this and shuts off the fuel supply. A vapor space above the liquid remains in the tank. This is called the ullage space, and is necessary to permit expansion of the liquid as it slowly starts to warm up. For safety, the tank incorporates a check valve and excess flow valve to stop the flow of LNG in the event of a line rupture.
|