免职声明:本网站为公益性网站,部分信息来自网络,如果涉及贵网站的知识产权,请及时反馈,我们承诺第一时间删除!
This website is a public welfare website, part of the information from the Internet, if it involves the intellectual property rights of your website, please timely feedback, we promise to delete the first time.
电话Tel: 19550540085: QQ号: 929496072 or 邮箱Email: Lng@vip.qq.com
摘要:This report describes an eva luation conducted by the Energy Information Administration (EIA) in August 2003 of two methods that estimate natural gas production in Texas. The first method (parametric method) was used by EIA from February through A..
|
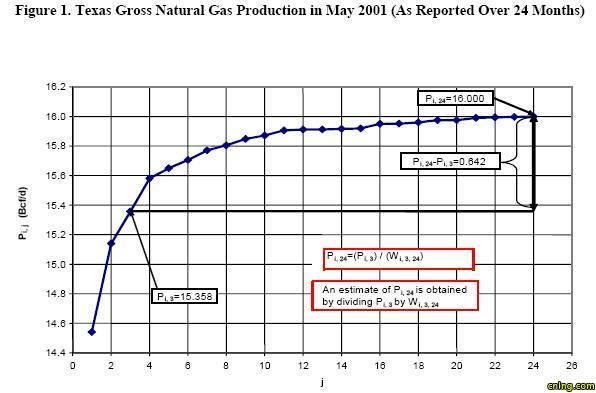
This report describes an eva luation conducted by the Energy Information Administration (EIA) in August 2003 of two methods that estimate natural gas production in Texas. The first method (parametric method) was used by EIA from February through August 2003 and the second method (multinomial method) replaced it starting in September 2003, based on the results of this eva luation.
|